Network Shield
The SCONE Network shield can limit the network communication of an application. When enabled in the policy, only explicitly permitted network communication is allowed. (This feature is available starting SCONE 5.8)
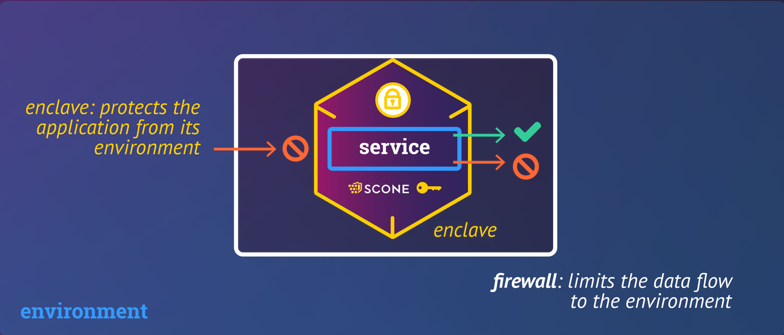
The Network Shield can protect network connections of a service executed with SCONE. It provides
- transparent encryption: TLS-based encryption with mutual authentication guarantees confidentiality, integrity, and controlled access
- an application-level firewall: The shield can be configured to filter inbound and outbound network connections according to authorization rules
By default, the Network Shield is in unprotected mode and allows all communication to pass through unmodified. One needs to enable the network shield in the SCONE policy (aka session) of a confidential service.
Currently, the network shield can protect TCP connections and Unix sockets with a pathname. It can prevent all other network communication like UDP-based communication.
Configuration
The Network Shield can be configured through environment variables defined within the policy of a confidential application.
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD |
Determines mode of operation for all connections that are not explicitly configured. One of the following values:
|
If there is at least one SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_* variable set: unprotected. Otherwise: disabled |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_UNSUPPORTED_PROTOCOLS |
Determines how to handle protocols that are not yet supported by the Network Shield (e.g. UDP). One of the following values: unprotected - Connections remain unfilteredrefuse - Connections are refused |
unprotected if SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD is unprotected, refuse if SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD is protected |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_<name>, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1 |
Mode of operation for a server port (determined by SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_<name>_PORT). One of:
|
No default |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_<name>_PORT, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1_PORT |
<IP protocol>:<port>, e.g. TCP:8080, or unix:<pathname>, e.g. unix:/var/run/myapp/unix_socket |
No default |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_<name>_IDENTITY, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1_IDENTITY |
X.509 server identity (concatenated PEM-encoded PKCS#8 private key, X.509 end-entity certificate, and optionally chain CA certificates). Only applicable if this server port's mode is protected. |
If omitted, an ephemeral server identity will be generated. |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_<name>_CLIENT_AUTH, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1_CLIENT_AUTH |
Client authentication mode. Only applicable if this server port's mode is protected. One of:
|
No default |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1 |
Mode of operation for an outbound connection (determined by SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_DESTINATION and SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_DESTINATION_IP/SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_SERVER_DNS_NAME). One of:
|
No default |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_DESTINATION, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_DESTINATION |
<IP protocol>:<DNS name>:<port>, e.g. TCP:db.mycluster.local:8080, or unix:<pathname>, e.g. unix:/var/run/myapp/unix_socket |
No default |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_DESTINATION_IP, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_DESTINATION_IP |
Required when using IP sockets. Not required when using Unix sockets. One of:
|
No default |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_SERVER_DNS_NAME, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_SERVER_DNS_NAME |
Required when using protected Unix sockets. Not required when using IP sockets (already included in DESTINATION). Though Unix sockets always refer to the local machine, the Network Shield still verifies DNS names in server certificates to ensure the correct certificate is presented. You can use any arbitrary name. |
No default |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_IDENTITY, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_IDENTITY |
X.509 client identity (concatenated PEM-encoded PKCS#8 private key, X.509 end-entity certificate, and optionally chain CA certificates). Only applicable if the mode is protected. |
If omitted, no client identity will be used. |
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_<name>_SERVER_AUTH, e.g. SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_SERVER_AUTH |
Client authentication mode. Only applicable if the mode is protected. One of:
|
No default |
All of these environment variables can be set within SCONE CAS policies using secret injection (which is recommended for certificates and private keys).
A future version of the Network Shield will feature a more streamlined session integration focusing on service mesh architectures.
Example
Here are some examples of how to configure the network shield:
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD=protected
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1="protected"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1_PORT="TCP:8080"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1_IDENTITY="
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_1_CLIENT_AUTH="
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_2="unprotected"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_2_PORT="TCP:443"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_3="protected"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_3_IDENTITY="[...]"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_3_CLIENT_AUTH="disabled"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_SERVER_3_PORT="unix:/var/run/myapp/unix_socket"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1="protected"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_DESTINATION="TCP:db.mycluster.local:8080"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_DESTINATION_IP="192.168.4.19"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_IDENTITY="
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_SERVER_AUTH="
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_2="unprotected"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_2_DESTINATION="TCP:log.mycluster.local:443"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_2_DESTINATION_IP="192.168.4.9"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_3="protected"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_3_DESTINATION="unix:/var/run/myapp/unix_socket"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_3_SERVER_AUTH="[...]"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_3_SERVER_DNS_NAME="dns.name.from.certificate"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_3="unprotected"
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_3_DESTINATION="unix:/var/run/myapp/other_socket"We recommended to inject the certificates and private keys: one defines theses in the the secret section (e.g., secret named mycertificate) and then uses these as $$SCONE::mycertificate:crt$$.
Example 2
Consider that we want to ensure that a confidential service cannot communicate with any other services. For example, the service might read encrypted files and write encrypted files but is not expected nor permitted to communicate via the network. The network shield can enforce this with the following configuration:
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD = protected
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_UNSUPPORTED_PROTOCOLS = refuseLimitations
Configuration and Certificates:
- Certificates listed in the
*_SERVER_AUTHand*_CLIENT_AUTHvariables must be CA certificates - Server and client certificates set in
*_IDENTITYvariables must be X.509v3 certificates with a valid Subject Alternative Names (SAN) extension - There is currently no way to configure abstract or unnamed Unix sockets (only Unix sockets with a pathname are supported)
- Unix sockets require an (arbitrary) DNS name (variable
SCONE_NETWORK_SHIELD_CLIENT_1_SERVER_DNS_NAME) - Port or pathname configuration must match exactly between server and client. For example, if network address translation (NAT) changes port numbers, the connection will not be accepted. Similarly, the connection will not be accepted if the client uses a different pathname, even if it points to the same Unix socket (e.g., through a symbolic link). This precaution prevents port misdirection attacks (when multiple ports use the same certificate), implemented through the TLS ALPN (application-layer protocol negotiation) extension.
- If an external (non-Network-Shield) TLS server or client uses the TLS ALPN extension, the connection will fail due to an ALPN mismatch. Please remove the ALPN extension as a workaround.
Application Compatibility:
- When used together with external clients or servers, they must not send an ALPN extension; otherwise, the connection will fail with a protocol mismatch error (in the debug log with
SCONE_LOG=debug, entrypeer doesn't support any known protocolcan be found)
System Calls:
- The Network Shield only supports TCP and Unix sockets at the moment
- Not all system call options and flags are supported. Notably, this includes Out-of-Band and ancillary data.
- At the moment, select/poll/epoll may indicate sockets to be readable or writable when they are not.
- Edge-triggered
epolldoes not work for protected connections - After a
fork, either the parent or the child may continue to use protected connections. Attempting to read or write from both processes will lead to TLS errors. - After an
execve, protected connections only remain usable if they have been connected but not written to or read from in the parent. Attempting to perform I/O in both processes will lead to TLS errors.